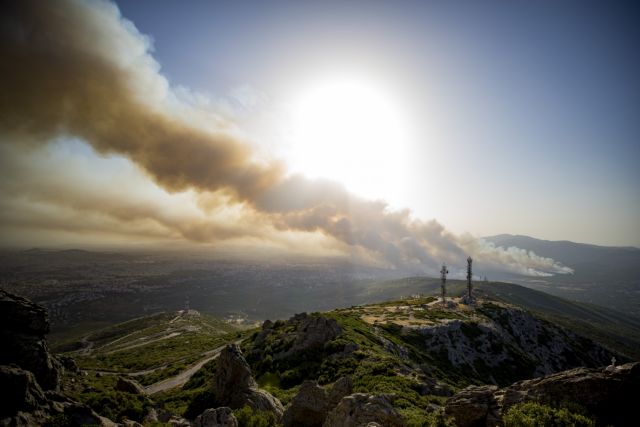

The smoke from the extensive fires in Greece has aggravated the atmospheric conditions even in remote areas, such as Antikythera, as shown by a study of the ReaCT team of the Institute of Astronomy, Astrophysics, Space Applications and Remote Sensing (IAAKEO) .
According to the records of the PANGAIA Observatory of the National Observatory in Antikythera, the load of suspended smoke particles in the atmospheric column is six times higher than the average observed in August.
Also, according to the Institute’s measurements, which have been included in the NASA-AERONET network, the layers of smoke are transported to remote areas at altitudes of up to 3 km, affecting atmospheric conditions at distances as far as Africa.
Latest News

Rhodes Airport Tops Fraport Greece’s Regional Airports in 2024 Performance
According to Fraport's data, more than 35 million passengers (specifically 35.2 million) were handled by Fraport-managed airports during the 11 months.

European Central Bank Cuts Interest Rates by 25 Basis Points
It is the fourth cut of interest rates by Europe’s central bank, a move expected by the markets and financial analysts leading to the rate settling at 3%.

Airbnb: New Measures Add €600 in Extra Costs for Property Owners
Property managers face an immediate administrative fine of 5,000 euros if access to the inspected property is denied or any of the specified requirements are not met.

Economist: Greece Included in the Best Performing Economies in 2024
Meanwhile, Northern European countries disappoint, with sluggish performances from the United Kingdom and Germany.

EasyJet Expands Its Routes from Athens
The airline’s two new routes will be to London Luton and Alicante and they will commence in summer 2025.

Capital Link Forum Highlights Greece’s Economic Resurgence; Honors BoG Gov Stournaras
Capital Link Hellenic Leadership Award recipient, Bank of Greece Gov. Yannis Stournaras, an ex-FinMin, was lauded for his pivotal role during Greece’s economic recovery

Tourist Spending in Greece Up by 14%, Visa Card Analysis Shows
Greece’s capital Athens emerged as the most popular destination, recording a 17% increase in transactions with Visa cards, surpassing even the cosmopolitan island of Mykonos.

Inflation in Greece Unchanged at 2.4% in Nov. 2024
The general consumer price index (CPI) posted a 0.4% decrease in November compared to the previous month

2024 Christmas Holidays: Extended Shop Hours Schedule
The 2024 Christmas Holidays extended shop hours schedule commences on Thursday, December 12 and runs until the end of the year.

ELSTAT: Seasonally Adjusted Unemployment Down in October
The number of employed individuals reached 4,284,694, an increase of 67,723 compared to October 2023 (+1.6%) and 22,002 compared to September 2024 (+0.5%).














![Fraport: Πάνω από 35 εκατ. επιβάτες στα αεροδρόμια το 11μηνο – Πτώση στη Μύκονο [πίνακας]](https://www.ot.gr/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/fraport-90x90.jpg)
























 Αριθμός Πιστοποίησης Μ.Η.Τ.232433
Αριθμός Πιστοποίησης Μ.Η.Τ.232433